introduction LED light source has the advantages of small volume, anti-vibration, DC low voltage, safety, easy dimming control, high luminous efficiency, rich color, long life and environmental protection. It is developed after the incandescent lamp, fluorescent lamp and high-pressure gas discharge lamp in the history of illumination. A major leap. Especially in the early 1990s, Japanese researcher Nakamura Shuji successfully developed a homogenous junction GaN blue LED with Mg and a breakthrough in rare earth yellow phosphor, which laid the foundation for the white LED light source to enter the general lighting application, causing domestic The external optoelectronics and lighting industry has a broader focus. With the rapid development of epitaxial growth and chip manufacturing technology, the luminous efficiency of LEDs has been greatly improved. LED devices have also evolved from early indicator LEDs (constant current 20mA) to power LEDs (constant current 350mA, 700mA or higher). . However, there are still many problems in the replacement of traditional illumination sources by LED light sources. According to statistics, in 2010, LED lighting products accounted for a small proportion of the national lighting market, and the output value only accounted for 3.2%. This paper attempts to explore the barriers in the development of LED light sources, from the aspects of luminous efficiency, heat dissipation, drive circuits, non-imaging optical design, cost and standards, in order to discuss and obtain corrections with colleagues. 1 Technical barrier 1. 1 luminous efficiency It is well known that the luminous flux of a single LED is limited, and one of the solutions is to improve its luminous efficiency. In general, the way to improve the luminous efficiency of LEDs is mainly to improve their internal quantum efficiency and external quantum efficiency. Internal quantum efficiency is the ratio of the number of photons generated by radiative recombination per second to the total number of electron-hole pairs recombined per second in the active region; External quantum efficiency is the photon emitted by the device per second. The ratio of the number and the number of electrons passing through the LED per second. The key to improving the internal quantum efficiency is to improve the epitaxial process of the crystal, reduce the misalignment of the crystal, and improve the quantum well structure by optimizing the quantum well width and other measures to further improve the chip quality and improve the device performance. To improve the external quantum efficiency, mainly from the perspective of chip technology, such as optimized substrate stripping technology, surface roughening technology and the use of photonic crystal structure, these technical measures can also improve the quantum efficiency of the chip. At present, the improvement of LED light efficiency has achieved remarkable achievements. The LED light efficiency developed by the laboratory has reached 230 lm / W, and the LED light effect of commercial mass production and market sales has reached 85 lm /W or even higher. The trend of LED light efficiency improvement is beyond the reach of traditional light sources. Based on current technical conditions and research and development levels, Philips Lumileds proposed in 2008 the efficiency of the future LED drive current up to 2A. As shown in Table 1. Table 1 shows that the phosphor conversion efficiency will reach 240 lm /Optical Watt in the future. For cool white LEDs, this is a achievable numerical level; but for warm white LEDs (CCT around 3 000K), this efficiency will be reduced by 10% to 20%. Therefore, it will be of great significance to improve the efficacy of LEDs by studying better LED phosphors. 1. 2 heat problem More than 70% of the energy supplied to the LEDs is converted into heat. Unlike conventional light sources, white LEDs contain almost no infrared light in the luminescence spectrum, so their heat cannot be released by infrared radiation. Since the heat is concentrated in a tiny chip (generally the chip size is in the range of 1mm × 1mm to 2.15mm × 2.15mm), the driving current of the power LED is generally 350mA, even up to 1A, which will cause heat accumulation inside the chip. The junction temperature rises, which significantly reduces the light output of the chip. If the junction temperature rises by 10 °C, the light efficiency and lifetime will drop by more than half; it will also cause the emission wavelength of the chip to drift, which will not match the excitation wavelength of the phosphor, reduce the lasing efficiency of the phosphor, and further reduce the white light. The luminous efficiency of the LED also accelerates the aging of the phosphor, which seriously affects the optical performance of the device. Therefore, the heat dissipation problem has become an aspect that must be paid attention to in the promotion and application of LED light sources. The thermal performance of LEDs is highly dependent on the package structure and packaging materials of the device. In view of the formal structure adopted by conventional LEDs, chip flipping technology has been developed to enhance heat dissipation. At the same time, due to the limitation of the mechanical strength and thermal conductivity of the silicon wafer material, the further improvement of the heat transfer performance of the LED requires matching of the new material; for example, the structure of the chip mounted on the PCB of the metal core and the heat dissipation by packaging onto the heat sink; The method, because the PCB in the interlayer is a poor conductor of heat, also hinders heat transfer. For materials such as bonding materials, phosphors, potting compounds, and heat-dissipating substrates used in packaging processes, bonding materials and heat-dissipating substrates are the key to LED heat dissipation. If the thermal conductivity of the selected thermal adhesive is poor, or the conductive silver paste is used to increase the brightness while heating too much, and lead-containing toxic metals, it will affect the performance of the LED. The substrate material may be a ceramic, a Cu/W plate or the like as a heat dissipating material. Recently, the Seoul Research Institute of South Korea reported that aluminum alloys with thermal resistance of a fraction of that of ordinary aluminum were available, but the production cost of these alloys was too high, which was not conducive to large-scale and low-cost production. LED package structure, packaging material, thermal paste coating and electrode soldering process will affect the heat dissipation capability of the chip side surface and the upper surface, so it must be given full attention and careful consideration. Most of the heat generated by the LED is transferred to the heat sink at the bottom of the chip by heat conduction, and then dissipated by heat convection. Therefore, the new heat pipe working medium formula uses high-efficiency heat transfer heat pipe device, which not only has high heat dissipation efficiency, compact structure and small volume, but also has free shrinkage at both ends of the heat pipe, small thermal stress, and double barrier between water vapor and heat source. It ensures safe leakage and low smoke resistance, is easy to clean and reduces energy consumption, so that heat pipe cooling technology is widely used in high-power LED lighting devices. For white light illumination systems that use multiple LEDs and are densely arranged, the heat management problem is more important because of the mutual influence of the modules. In addition to reducing the thermal resistance of the die at the chip level, the package material with high thermal conductivity should be used, and the design is more reasonable. Heat sink, optimized drive power, etc. to reduce the thermal resistance of the packaged device and improve device performance 1. 3 drive circuit In a complete LED application design, the design of the driver circuit is one of the core technologies. The main function of the drive circuit is to convert the AC voltage into a constant current source. The power type LED is usually operated by DC, and the working voltage is only about 3. 5V, but the working current is large. When designing the driving circuit, it is necessary to consider the single tube efficiency of the white LED, and also consider the overall conversion efficiency and complexity of the circuit. And cost. There is no doubt that the efficiency of the drive circuit affects the overall efficiency of the luminaire, but the pursuit of high drive circuit efficiency is limited by cost. For example, the LED constant current switching power supply has high efficiency and is currently the most suitable LED driving circuit, but its high cost hinders its promotion and application. High-quality LED driver circuit design not only needs to meet specific electrical requirements, but also has high efficiency and high reliability, and can work at higher temperatures, but the implementation of these requirements is often limited by cost. A suitable LED light source operating circuit should be a versatile component that encapsulates the drive, protection and control circuitry, as well as the auxiliary power sensor and passive components into a single unit. Recently, the Seoul Research Institute of Korea announced the development of an LED light source that is directly driven by 220V AC, but its light efficiency is flawed, and we look forward to its new progress and development. 1. 4 non-imaging optical design Due to its small size and compact structure, the LED chip has a relatively small light-emitting area. It is a 180° Lambertian light source whose intensity distribution is proportional to the cosine of the exit angle, that is, the light emitted by the LED light source. The illuminance formed on the illuminated surface is rapidly attenuated as the exit angle increases. Obviously, such light source characteristics are difficult to meet the actual needs of lighting applications. Therefore, it is necessary to perform secondary optical design on the characteristics of the LED light source according to different applications and requirements, thereby realizing the shaping of the light emitted by the LED chip, especially For the distribution of light intensity. Such a secondary optical design process is actually in the category of non-imaging optical design. Compared with the design of imaging optical systems that care about the transmission of light source information, non-imaging optical system design is concerned with the utilization of light source energy and light distribution control. Due to the compact structure and high energy efficiency of the non-imaging optical system, it has attracted widespread attention in the design of LED lighting systems, which plays a decisive role in achieving the required light distribution of the LED lighting system on the illuminated surface. Nowadays, the company has introduced a new type of LED street lamp product, which puts a transparent plastic cover designed with non-imaging optical concept in front of each single LED, and then can install such a single LED on the heat dissipation plane. LED street lights that meet road lighting requirements without the need to configure mirrors with optical design. Of course, designing a non-imaging optical packaging system that meets the requirements of three-dimensional given light distribution applications is still one of the key technologies for LED light sources to enter the lighting market to replace traditional light sources. This is also a good starting point for promoting the promotion and application of LED lighting technology. 2 cost High cost is an unavoidable problem in the promotion and application of LED. The one-time investment and product cost performance are important reasons for the popularity of LED lighting. To generate 1 000 lm of luminous flux, the cost of incandescent lamps is less than 5 yuan; the cost of compact fluorescent lamps is less than 10 yuan; for LED light sources, ten high-power LEDs are required, costing more than 100 yuan. The cost of LEDs is closely linked to the resolution of LED technology bottlenecks, and breakthroughs in key technology bottlenecks will undoubtedly lead to a significant drop in LED costs. In 2009, a LED 863 project funded by up to 5 million yuan in China required the development of an LED light source that produced 1 000 lm of luminous flux, and the cost should be 40 yuan.
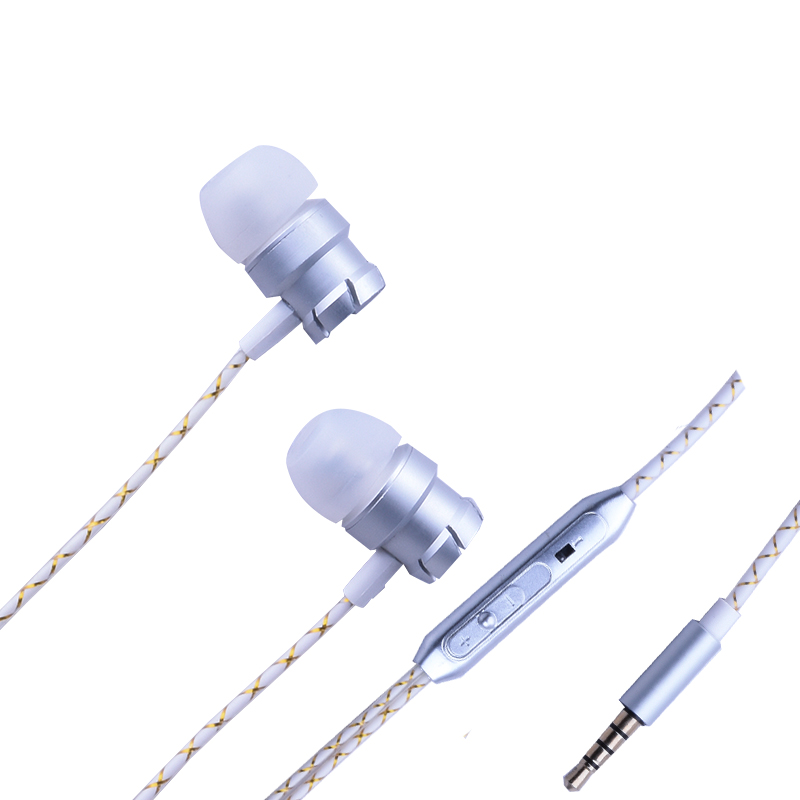
In-ear earphones are sometimes referred to as earbuds, and they refer to earphoees that are small enough to fit into the ear. The Sport Earphone are written with L and R, L is left for the left channel, and R is the right for the right channel. In principle, the thinner the earmuffs, the more comfortable they are. However, the thin earmuffs will be less soundproof.
Correct use:
1: Set the volume of the source to the minimum.
2: Insert the 3.5mm plug of the in-ear earphone into the earphone jack.
3: Adjust the volume to a position that sounds comfortable. In-ear earphones are not recommended for driving motorcycles, bicycles, operating machines, and jogging, as you may affect your judgment of potential hazards.
4: Do not open the volume too much during use.
5: When pulling the earphone plug, you should pinch the hard plastic part of the back end of the plug and pull it out, instead of pulling it straight out through the wire.
6: Avoid excessive bending of the wire for a long time.
In Ear Headphones,Sport Earphone,In Ear Earphones,Zipper In Ear Headphones Shenzhen Linx Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.linxheadphone.com