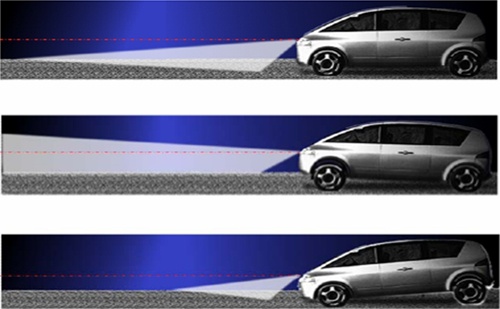
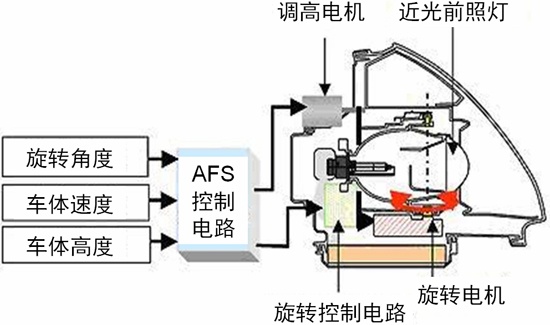
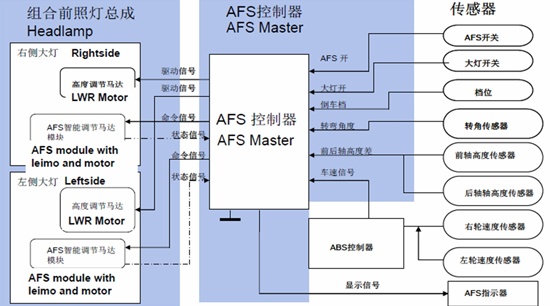
In recent years, with the advantages of increased light efficiency, low energy consumption, high reliability, long life, small size and environmental protection, LEDs have been increasingly used in automotive interior and exterior lighting, and have been less critical from automotive lighting applications. Such as cockpit lighting, parking lights and dashboard backlights, spanning a wider range of applications such as headlamps and combined taillights. In particular, due to its small size, LEDs can be combined with a wide variety of shapes and lines to help enhance the recognition of the lights. They are specified for the headlight system of many medium and high-end cars, with a beautiful appearance design. Figure 1 shows a typical automotive LED lighting application today. Figure 1: Typical automotive LED lighting applications Automotive LED lighting - not only beautiful, but also promotes active safety of the car The intuitive benefits that LED lighting brings to cars are not limited to beautiful shapes. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) and the European Commission (EC), although only 25% of driving is during nighttime and lack of light, 40% of deaths and serious injuries occur during this time. Therefore, improving the lighting of automobiles, especially at night and under light conditions, can help improve the active safety of the car. In fact, in order to protect the safety of drivers/cars/roadside pedestrians, the industry has long been committed to developing various automotive lighting solutions, such as adaptive headlamps (AFS) solutions for improving nighttime cornering, and Daytime running light (DRL) program for improving daytime driving safety. Compared to incandescent lamps and high-intensity gas discharge lamps (HID), which are traditionally used in automotive lighting, LEDs have unparalleled advantages for automotive lighting. If the LED response time is short, the brake light can increase the braking distance of the rear car, and the steering light has better warning effect. The brightness of the LED is high, but it is not as dazzling as HID, which helps to reduce the risk of dazzling the driver of the opposite car. LED lamps consume much less energy than incandescent lamps or HIDs, helping to reduce fuel consumption and save money. Typical automotive lighting application LED driver solution Different automotive lighting applications have different requirements for LED current, so it is necessary to select a suitable LED driver solution according to specific application requirements. Typical LED driver solutions include resistors, linear constant current regulators, linear regulators, and switching regulators. Among them, the resistor is the simplest and lowest cost LED current limiting scheme, but the energy efficiency is also the lowest, and there are problems such as LED screening cost and thermal runaway. Constant current regulator (CCR) performance is higher than the resistor scheme, but the cost is lower than the linear or switching regulator scheme, suitable for low current LED lighting applications. The linear regulator supports multiple lines in parallel configuration to help dissipate heat, providing ±2% steady-state accuracy, no electromagnetic interference (EMI) problems, medium cost, but low energy efficiency. Switching regulators are widely used. This solution is more costly and more complex, but supports any type of input voltage vs. output voltage, and energy efficiency can be higher than 90% depending on input/output conditions, but there are EMI issues. Figure 2: Typical Automotive Lighting Applications and LED Driver Solutions In addition to these solutions, ON Semiconductor also introduced a highly integrated LED Lighting Management Integrated Circuit (LMIC). These LMICs integrate a variety of LED drive and control functions, equivalent to a complete subsystem that can withstand ambient temperatures up to 125 ° C for automotive headlamps, combined taillights and the latest AFS applications. Application Advantages and Working Principles of Adaptive Headlamp System (AFS) The light of the traditional car headlights is always consistent with the direction of the car body. When the car turns, it cannot effectively illuminate the blind spot inside the curve. If there is a person or object inside the curve, and the speed is not properly lowered, it will bring safety hazards. As shown in Figure 1. In comparison, the AFS function provides a swiveling adjustment that rotates at the angle of the steering wheel to project an effective beam onto the front surface that the driver needs to see to help reduce safety hazards. Figure 3: Rotation adjustment (left) and horizontal adjustment (right) of the AFS function. In addition to dynamic rotary adjustment, the AFS function provides dynamic level adjustment. This function adjusts the headlight level according to the signal of the load axis sensor, which can adapt to different loads and different slope environments. As shown in the right side of Figure 1, the above picture shows the effect of the AFS function on the light level under normal conditions. The middle picture shows the effect of the light up under the bumpy conditions of the car when starting or going uphill. The picture below is under braking or downhill conditions. The lighting level sinks the lighting effect. It can be seen that AFS can dynamically adjust the light height according to the horizontal tilt of the vehicle body to improve the lighting effect and enhance safety. The structure diagram of AFS working principle is shown in Figure 2 and Figure 3, respectively. Figure 4: Structure diagram of the working principle of AFS.
2.5 Inch LED Downlights can be detachable in two parts. The module and 2.5 Inch size rings.
For the 2.5 Inch LED Downlights' module, it can be do for 5W and 9W. That is, for the size of 2.5 Inch LED Downlights, we can do 5W and 9W.
Black color for module. White, black, silver color for ring. Color temperature (CCT): 2600-2700K, 2800-3200K, 3800-4200K, 5000K-5500K, 6000-6500K.
AC100-240V. 50Hz. With Philips / Lifud / Go-color / Leipo driver.
For the 2.5 Inch downlights, inner diameter is 75mm. Outer diameter is 95mm. Height is 50mm. It can be embed into 75-110mm cut out hole size.
High CRI, hight PF, 5W cool white flux can be reach 494lm. 120° beam angle.
Dimmable or Non-dimmable function are available.
2.5 Inch Led Downlights 2.5 Inch LED Downlights, 3000K 2.5 Inch LED Downlights, 5W 2.5 Inch LED Downlights, White 2.5 Inch LED Downlights SHENZHEN KEHEI LIGHTING TECHNOLOGY CO.LTD , https://www.keheiled.com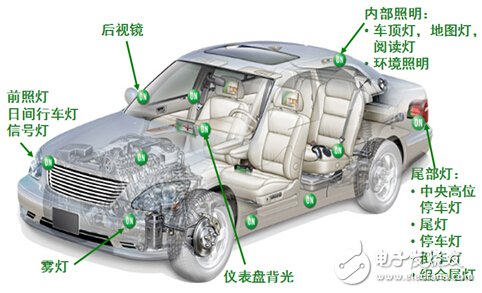




Automotive lighting typical application and LED lighting drive solution collection
Figure 5: Structure of the working principle of AFS